Sep 12,2024
N-bromosuccinimide, also known as N-bromosuccinimide, English name: N-bromosuccinimide, referred to as NBS, is an important bromination agent in organic synthesis. It has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, good selectivity, high yield, easy separation of products, etc., and is used in the free radical bromination reaction of allyl and benzyl. Electrophilic bromination of ketones, aromatic compounds or heterocyclic compounds and addition of olefins; Also as a catalyst, oxidizer and other aspects have a wide range of applications, is the chemical and pharmaceutical industry commonly used bromination reagent. N-bromosuccinimide, as an important intermediate in medicine, pesticides and organic polymer materials, has wide applications and broad market prospects, and plays an irreplaceable role in chemical, pharmaceutical and organic polymer materials industries.
【 Physical and chemical properties 】
N-bromosuccinimide is white or milky white fine crystal at room temperature, with a microodor of bromine. Melting point 180 ~ 182 ℃, specific gravity 2.097, soluble in acetone, ethyl acetate, acetic anhydride, insoluble in water, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, chloroform, etc.
【 Preparation method 】
1. Bromine reacts with succinimide base solution, resulting in uneven product quality, low utilization rate of bromine resources and high production cost; Specific experimental steps: Dissolve succinimide in a solution of sodium hydroxide, crushed ice and water, and add liquid bromine under the condition of ice water bath. After the reaction, the crude product was washed with ice water to remove the remaining bromine and dried to obtain N-bromosuccinimide. Purity :90% ~ 97%. mp:173 ~ 175℃, 180 ~ 183℃(decomposition), the reaction formula is as follows:
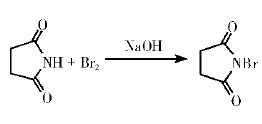
FIG. 1 shows the formula for the synthesis of N-bromosuccinimide by method 1
2. Reaction with sodium bromate, hydrobromic acid, succinimide, hydrobromic acid volatile, serious pollution, and domestic hydrobromic acid concentration is different, the production process is not easy to control;
3. The process of synthesizing n-bromosuccinimide with succinimide, sodium bromate, sodium bromide and sulfuric acid, but there is no specific operation process, no specific raw material ratio and feeding sequence, and the feeding amount is milligram grade, which cannot provide a reliable reference for industrial production.
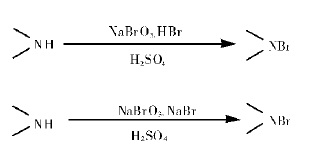
Figure 2 shows the reaction formula of N-bromosuccinimide synthesis in Method 2
4. Experimental steps for the synthesis of N-bromosuccinimide with sodium bromate, sodium bromide, sulfuric acid and succinimide as the main raw materials: Under the condition of 25℃ and agitation, 17.8g(180mmol) succinimide and 10.4g(69mmol) sodium bromate were dissolved into 60mL water, 6.6mL sulfuric acid was added, 14.2g(138mmol) sodium bromide solution was added, and after the addition, the reaction was stirred for 2.5h, filtered and dried. The yield of 27.9 gn-bromosuccinimide was 87%.
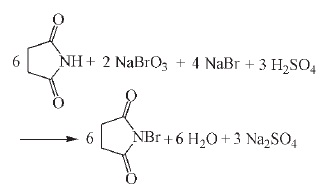
Figure 3 shows the reaction formula of N-bromosuccinimide synthesis in Method 4
【 Application 】
1.NBS allyl, benzyl reaction N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) is a mild bromine reagent, it is suitable for the bromine reaction of the allyl and benzyl sites, not only the reaction conditions are mild, easy to operate, but also the reaction selectivity is high and the side reaction is less.
2. Reaction on the aromatic ring of NBS NBS can be brominated with aromatic ethers (such as anisole, m-anisole, α-naphthalene methyl ether, etc.). With a small number of Friedel-Crafts reaction catalysts, such as aluminum trichloride, zinc chloride or iron, benzene and toluene can also be benzene cyclobrominated with NBS to obtain bromobenzene and p-bromotoluene, respectively.
3.NBS addition reaction to olefin Under the catalysis of acid, the addition of n-bromosuccinimide to olefin is an important method to prepare β-halogenated alcohols. The method has high stereoselectivity, high yield, pure product, mild reaction and easy operation. The yield reached 82%. The reaction formula is as follows:
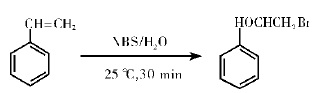
Figure 4 shows the reaction formula for preparing β-halogenated alcohols
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is a very effective solvent. Using NBS to react with olefin in aqueous DMSO, a highly stereoselective addition product with a good yield of 92% can be obtained. The reaction formula is:
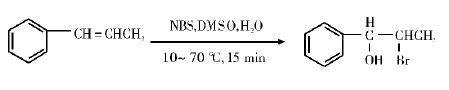
4.NBS carbonyl α-site reaction NBS is a very good carbonyl α-site bromine reagent, the reaction is easy to operate, widely used. In order to increase the reaction rate and yield, many catalytic systems have been developed. Rapid bromination of 1, 3-dicarbonyl compounds in NBS catalyzed by Mg(ClO4)2. The reaction proceeds gently in CH3CN or EtOAc. The reaction has good stereoselectivity, and it can be very convenient to prepare α-bromo1, 3-dicarboxylic compounds which are very important in organic synthesis.
5. Other uses The traditional applications of N-bromo-succinimide reagents in organic reactions are the bromo-hydrides of allyl, benzyl and carbo-alpha-hydrides. With the deepening of research, it is gradually found that NBS can be applied in many aspects such as catalyst and oxidizer.
(1)NBS as catalyst, using NBS as catalyst, using toluenesulfonamide and alcohols as nucleophiles to react on active styrene under mild conditions to obtain amino (yielDS60%-83%) and alkoxy derivatives (yields75%-85%), respectively. Both of these reactions have high yields and 100% use Markov addition. Ethanol was acetylated with acetic anhydride using NBS as catalyst. The reaction was carried out at room temperature with chloroform as solvent. The yield was high and the byproducts were few.
(2)NBS is used as an oxidizing agent to oxidize many secondary alcohols to ketones. The reaction was catalyzed by cobalt complex of acetyl acetone.
Active polymerization is a very important method for preparing polymers with specific structures and narrow molecular weight distributions. Because the N-Br bond in NBS is very active, it is easy to break under heating to obtain active succinimide free radicals and inert bromine free radicals. Therefore, it is possible to use NBS as the chain-initiated transfer terminator of radical polymerization.