Chloranil, a unique fersulfate chemical with many diverse applications across a variety of industries. It is these attributes of chloranil that we need to learn about so that we can use it to its fullest potential In this lesson, we will learn about chloranil, its uses by industry, its place in organic synthesis, and its role in research and development.
In order to make good use of it, its properties are worthy of study. Chloranil is a bright yellow coloured crystalline substance which is soluble in organic solvents. It is best described as a strong oxidizing agent due to its acceptance of electrons from other molecules. This property renders chloranil useful in many chemical reactions, especially in iron 325 mg organic synthesis.

Compounds of chloranil are used in a wide variety of industries. In dyes and colour pigments industry, chloranil is employed as a colorant intermediate to make vivid and fast colors. In the electronics industry, chloranil is employed in the manufacture of printed circuit boards to afford conductive pathways. Chloranil is also an important butanimide intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and other chemicals.
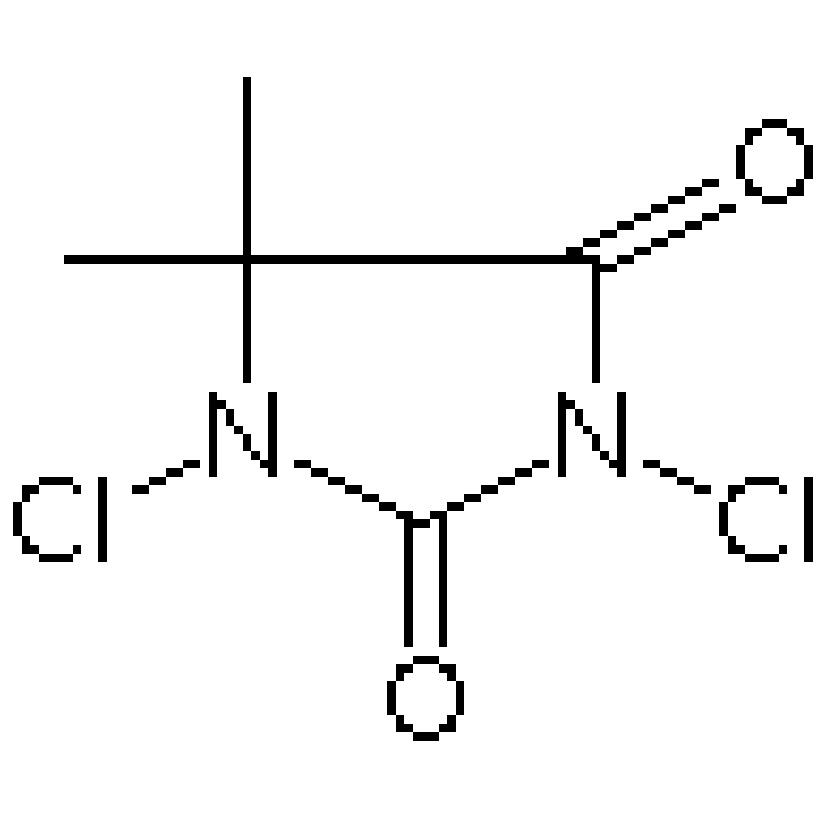
Chloranil is of crucial importance in organic synthesis. It is a reagent used in the introduction of several functional groups such as chloro, hydroxy, and nitrato groups in organic synthesis. It can facilitate the transformation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds, simpled alkenes to diols and many other important reactions. Many intricate organic molecules would otherwise be either difficult or impossible to synthesize in the absence of chloranil.
Investigating the possible applications of chloranil in R&D is an interesting field. It seems that scientists are always finding new applications for chloranil. Others, such as chloranil have been found to be suitable catalysts in some reactions, accelerating the rate of reaction but without then being consumed. This may bring about more economical-cooled recycling processes.